Respiratory System In Birds
Respiratory system of birds is relatively different in mechanism and structure from mammals. They have most efficient respiratory system as they need continuous supply of oxygen due to high metabolic rate required for flight. Efficiency of birds respiratory system is because all the time fresh air is supplied to �Parabronchi� , the site for exchange of gasses(birds don�t have alveoli in their lungs as in mammals rather have these tiny passages opened at both end, connected to air sacs on both sides ).
Anatomy of avian show unique respiratory system adaptations. Avian lungs are small as compared to mammals. Most of volume is occupied by air sacs and parabronchi are the sites for gaseous exchange. Avian have larynx yet it does not have any role in voice production instead �Syrinx� in birds does the job and is called the voice box.
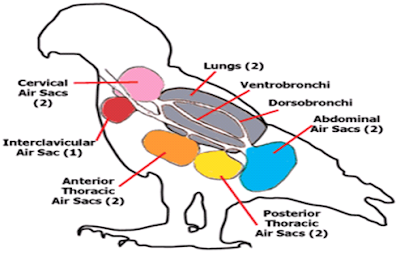
Air sacs (that are just extensions of lungs) have very thin walls with few blood vessels. So, they do not play a direct role in gas exchange. Rather, they act as a 'bellows' to ventilate the lungs. Mostly birds have 9 air sacs (depending upon the species)
- Thoracic(two posterior thoracic and two anterior thoracic)
- Two abdominal
- Two cervical(not present in some species)
- One interclavicular
Now the thing that baffles most of us is �working of air sacs and parabronchi and how parabronchi are said to be open at both ends?� Well the situation of air sacs can be made clear by above diagram showing all the air sacs. The grey area is lungs and have very thin walled parabronchi instead of alveoli. Birds have an incomplete diaphragm and the arrangements of the chest musculature and the sternum do not lend themselves to expand in the same way that the chest of mammals does. Consequently birds can�t inflate and deflate lungs in the same way as mammals do. Air is moved in and out of the respiratory system through pressure changes in the air sacs. Muscles in the chest cause sternum to move upward and outward , decreasing pressure inside and air passively enters into the lungs (here too partial pressure difference aids the movement). Although expiration is not passive, but requires certain muscles to put pressure on air sacs to expel air out through nostrils or mouth. Trachea divides into two primary bronchi after syrinx.
The above diagram shows why parabronchi are said to be open at both ends and why no stale of air remains in them because all the time fresh air is ventilated. Above diagram also depicts the pathway taken by air throughout respiration cycle. The key to the avian respiratory system is that distention and compression of the air sacs, not the lungs, moves air in and out.
Respiratory cycle:
Hope these diagrams do clear the pathway air takes during inspiration and expiration.
The air sacs permit a unidirectional flow of air through the lungs, (i.e. from trachea to caudal sacs, parabronchi to cranial sacs and out) air moving through bird lungs has a higher oxygen content. In contrast, air flow is 'bidirectional' in mammals, moving back and forth into and out of the lungs. As a result, air coming into a mammal's lungs is mixed with 'old' air (air that has been in the lungs for a while) & this 'mixed air' has less oxygen. Also in birds �counter current exchange occurs� i.e. blood in parabronchi flows in opposite direction than the direction of flow of air. Rate of respiration in avian in slower than in mammals.
Entry # 1
Written By Midhat Fatima



Comments
Post a Comment