NEPHRON
Human body is complex and not easy to understand completely until we understand its unit. Cell is the structural and fundamental unit of human body. By understanding cell, it is quite easy for us to understand human body.
Likewise, kidney also consist of small unit which combine together to form it. Nephron is functional unit of kidney.
Types of Nephron:
- Cortical nephron
- Juxtamedullary nephron
Cortical nephron:
The nephrons which are arranged along cortex of kidney are called cortical nephrons. Cortical nephrons produce dilute urine.
Juxtamedullary nephron:
The nephron which are arranged along the boundary of cortex and mainly in medulla are called juxtamedullary nephrons. They produce concentrated urine.
Structure:
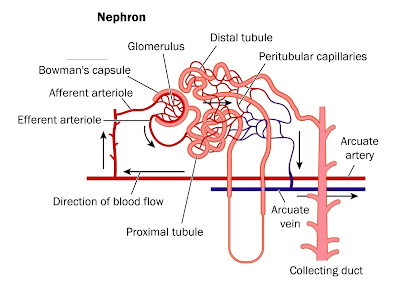
Nephron mainly consist of three main parts:
- Glomerulus
- Bowman�s Capsule
- Loop of Henle
Further, it contains:
- Afferent arteriole
- Efferent arteriole
- Proximal tubule
- Peritubular capillaries
- Distal tubule
- Collecting tubules
- Vasa recta
Glomerulus:
It is a compact ball of capillaries. Blood is passed from glomerulus to Bowman�s capsule for purification. Blood enters in glomerulus through Afferent arteriole and leaves through Efferent arteriole which is less in diameter than afferent arteriole . Due to this difference in diameter, more blood is coming and less is moving out which causes pressure filtration.
Efferent arteriole divides to form Peritubular capillaries.
Bowman�s Capsule:
It is a cup shaped structure present around glomerulus. Bowman�s capsule continues to form Proximal tubule.
Loop of Henle:
Proximal tubule continues to form Loop of Henle. It is a U shaped tube. It is surrounded by Vasa recta which are small straight capillaries. Loop of Henle ends at Distal tubule and Collecting tubules.
Working:
The working of nephron involves the passing of blood from glomerulus to the Bowman�s capsule. Glomerulus is a porous structure. From Bowman�s capsule blood moves towards the descending loop of Henle then reaches to ascending loop of Henle.
Working of nephron can be easily described in following three steps:
1. Filtration:
During filtration some useful materials like
- Glucose
- Amino acids
- Salts
- Water
also passes with wastes and some wastes remained in blood so to take useful material back in blood and to remove all wastes exchange of waste and beneficial materials take place between proximal tubule and peritubular capillaries.
2. Selective Reabsorption:
Transport of useful substances from lumen of proximal tubule into peritubular capillaries is selective reabsorption.
3. Tubular Secretion:
Transport of metabolic waste material from peritubular capillaries into the lumen of proximal tubule.
Hormones:
Following hormones are involved in movement of water and salts in and out of nephron.
Aldosterone:
It is secreted by adrenal cortex. Its function is active uptake of sodium in ascending limb of loop of Henle.
ADH (Anti Diuretic Hormone):
It is secreted from posterior pituitary lobe. Its function is to transport water into collecting tubules.
Entry # 3
By Nagina Anwar
Comments
Post a Comment